
Transmission media can be either guided (such as cables, fiber optics, or UTP,) or unguided when no physical connectivity is established between the sender and receiver (such as in the case of wireless connections.) The inherent physical limitations of the transmission media also account for the maximum bandwidth and error rate. These signals might consist of either digital signals (electrical pulses) or analog signals (continuous electromagnetic waves).ĭepending on the type and quality of the physical layer, these signals might be deteriorated due to several phenomena such as noise, attenuation, dispersion, and distortion.

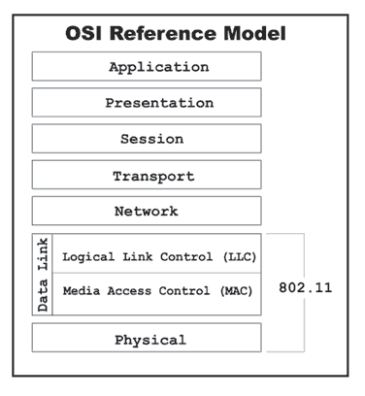
It translates the information that receives from the data-link layer (layer 2) into electromagnetic signals (binary data) to send them over the physical medium (wired or wireless media). Layer 1 is the first layer of the OSI Model, and therefore, the foundation upon which all higher-level functions are based. Network engineers can define different bit-transmission mechanisms for the physical layer level, including the shapes and types of connectors, cables, and frequencies for each physical medium. While the frequency range supported in Zigbee mostly 2.The physical layer is aimed at consolidating the hardware requirements of a network to enable the successful transmission of data. The frequency range supported in Bluetooth vary from 2.4 GHz to 2.483 GHz. IEEE standardizes all Zigbee-based protocols. The Zigbee Alliance is responsible for managing Zigbee and testing and approving Zigbee-based devices. The Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group) is the organization responsible for managing Bluetooth standards and devices. Besides these similarities, there are some differences which are given below in the tabular form. each run within the pair of.4-GHz unlicensed band, and each use tiny kind factors and low power. Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (CRAM)īoth Bluetooth and Zigbee have a lot in common which is, each area unit styles of IEEE 802.15 WPANs.AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting) configuration (locally).Computer Network | AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting).Service Set Identifier (SSID) in Computer Network.How Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) works?.ARP, Reverse ARP(RARP), Inverse ARP (InARP), Proxy ARP and Gratuitous ARP.Mobile Internet Protocol (or Mobile IP).Difference between Bluetooth and Zigbee.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
